|

Reference Guide
|
|
Introduction
Wireless Environment
 Operating modes
Operating modes
 Security
Security
 Radio signal range
Radio signal range
Operating modes
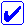
You can configure the network interface for the Infrastructure mode or the Ad Hoc mode.
In the Infrastructure mode, both wireless and wired computers can communicate through an access point to send data to the network interface.

 |
Note:
|
 | |
Some access points or routers support only the TCP/IP protocol. If you use this product with a protocol other than TCP/IP, make sure the protocols are supported by the access point or router.
|
|
In the Ad Hoc mode, a network interface and computers wirelessly communicate directly with each other, without using an access point.


[Top]
Security
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a security protocol for wireless network. Data is encrypted using the WEP Key providing the security of your wireless network. You must set the same WEP Key to the network interface and the access point.
The network interface supports a 64-bit or 128-bit encryption key, and you can use either hexadecimal or ASCII characters.
WPA-PSK(TKIP) is a Wi-Fi security with a strong encryption algorithm as well as user authentication. It provides a high security that user data remains protected and that only authorized users may access the network.
 |
Note:
|
 | |
The wireless transmission speed is reduced when WEP or WPA-PSK(TKIP) is enabled because time is required for encryption and decryption.
|
|
SSID is a unique identifier to specify a wireless LAN. All devices and access points connected to a specific wireless LAN must use the same SSID to communicate with devices on the wireless LAN.

[Top]
Radio signal range
The data transfer rate of the network interface depends on the environment where the network interface is located.
 |
Note:
|
 | |
The wireless transmission speed decreases as the distance between the network interface and the computer or the access point increases.
|
|

[Top]
| Version 1.00E, Copyright © 2003, SEIKO EPSON CORPORATION |
![]()
Operating modes
Security
Radio signal range



